در حال حاضر محصولی در سبد خرید شما وجود ندارد.
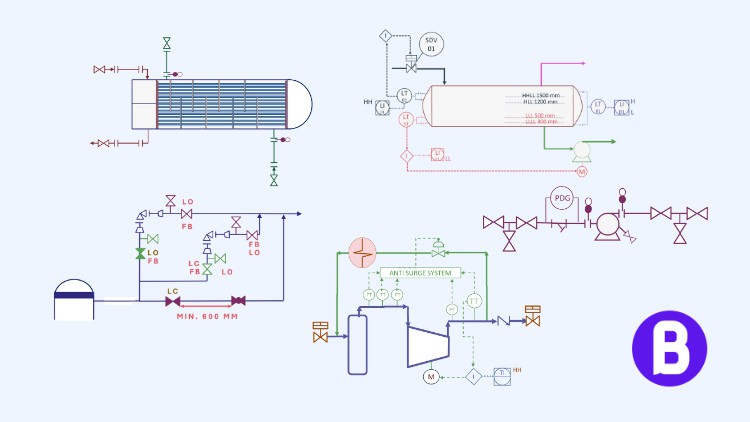
Discover the details, operation, maintenance, and safety guidelines of piping and instrumentation diagrams
در این روش نیاز به افزودن محصول به سبد خرید و تکمیل اطلاعات نیست و شما پس از وارد کردن ایمیل خود و طی کردن مراحل پرداخت لینک های دریافت محصولات را در ایمیل خود دریافت خواهید کرد.

✨ تا ۷۰% تخفیف با شارژ کیف پول 🎁
مشاهده پلن ها