1 - Chapter 1 Introducing data structures
2 - Part 1. Improving over basic data structures
3 - Chapter 1 Describing a data structure
4 - Chapter 1 Packing your knapsack - Data structures meet the real world
5 - Chapter 1 Algorithms to the rescue
6 - Chapter 2 Improving priority queues - d-way heaps
7 - Chapter 2 Solutions at hand - Keeping a sorted list
8 - Chapter 2 Concrete data structures
9 - Chapter 2 Priority, min-heap, and max-heap
10 - Chapter 2 How to implement a heap
11 - Chapter 2 PushDown
12 - Chapter 2 Top
13 - Chapter 2 Heapify
14 - Chapter 2 Use case - Find the k largest elements
15 - Chapter 2 More use cases
16 - Chapter 2 Analysis of branching factor
17 - Chapter 2 Performance analysis - Finding the best branching factor
18 - Chapter 2 Interpreting results
19 - Chapter 2 The mystery with heapify
20 - Chapter 3 Treaps - Using randomization to balance binary search trees
21 - Chapter 3 Treap
22 - Chapter 3 A few design questions
23 - Chapter 3 Delete
24 - Chapter 3 Applications - Randomized treaps
25 - Chapter 3 Performance analysis and profiling
26 - Chapter 3 Profiling height
27 - Chapter 3 Profiling memory usage
28 - Chapter 4 Bloom filters - Reducing the memory for tracking content
29 - Chapter 4 Alternatives to implementing a dictionary
30 - Chapter 4 Concrete data structures
31 - Chapter 4 Binary search tree - Every operation is logarithmic
32 - Chapter 4 Implementation
33 - Chapter 4 Constructor
34 - Chapter 4 Applications
35 - Chapter 4 Why Bloom filters work
36 - Chapter 4 Performance analysis
37 - Chapter 4 Explanation of the false-positive ratio formula
38 - Chapter 4 Improved variants
39 - Chapter 5 Disjoint sets - Sub-linear time processing
40 - Chapter 5 Reasoning on solutions
41 - Chapter 5 Naive solution
42 - Chapter 5 Using a tree-like structure
43 - Chapter 5 Heuristics to improve the running time
44 - Chapter 5 Applications
45 - Chapter 6 Trie, radix trie - Efficient string search
46 - Chapter 6 Trie
47 - Chapter 6 Search
48 - Chapter 6 Insert
49 - Chapter 6 Keys matching a prefix
50 - Chapter 6 Radix tries
51 - Chapter 6 Search
52 - Chapter 6 Applications
53 - Chapter 6 String sorting
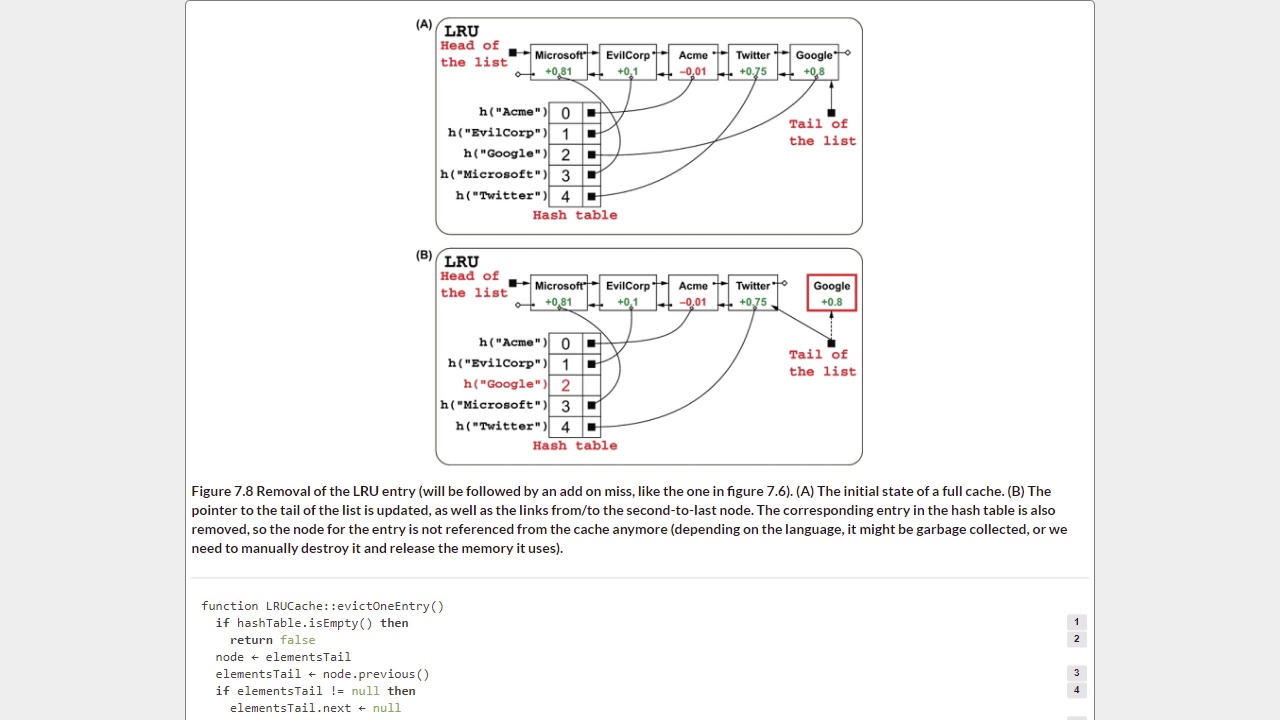
54 - Chapter 7 Use case - LRU cache
55 - Chapter 7 First attempt - Remembering values
56 - Chapter 7 Handling asynchronous calls
57 - Chapter 7 Memory is not enough (literally)
58 - Chapter 7 Getting rid of stale data - LRU cache
59 - Chapter 7 Temporal ordering
60 - Chapter 7 When fresher data is more valuable - LFU
61 - Chapter 7 How to use cache is just as important
62 - Chapter 7 Solving concurrency (in Java)
63 - Chapter 7 Read locks
64 - Part 2. Multidimensional queries
65 - Chapter 8 Nearest neighbors search
66 - Chapter 8 Simplifying things to get a hint
67 - Chapter 8 Moving to k-dimensional spaces
68 - Chapter 9 K-d trees - Multidimensional data indexing
69 - Chapter 9 Constructing the BST
70 - Chapter 9 Methods
71 - Chapter 9 Balanced tree
72 - Chapter 9 Remove
73 - Chapter 9 Nearest neighbor
74 - Chapter 9 Region search
75 - Chapter 10 Similarity Search Trees - Approximate nearest neighbors search for image retrieval
76 - Chapter 10 R-tree
77 - Chapter 10 Inserting points in an R-tree
78 - Chapter 10 Similarity search tree
79 - Chapter 10 SS-tree search
80 - Chapter 10 Insert
81 - Chapter 10 Insertion - Split nodes
82 - Chapter 10 Delete
83 - Chapter 10 Similarity Search
84 - Chapter 10 Approximated similarity search
85 - Chapter 10 SS+-tree
86 - Chapter 10 Reducing overlap
87 - Chapter 11 Applications of nearest neighbor search
88 - Chapter 11.Centralized application
89 - Chapter 11 Moving to a distributed application
90 - Chapter 11 Other applications
91 - Chapter 11 Multidimensional DB queries optimization
92 - Chapter 12 Clustering
93 - Chapter 12 Types of learning
94 - Chapter 12 K-means
95 - Chapter 12 The curse of dimensionality strikes again
96 - Chapter 12 Boosting k-means with k-d trees
97 - Chapter 12 DBSCAN
98 - Chapter 12 From definitions to an algorithm
99 - Chapter 12 And finally, an implementation
100 - Chapter 12 OPTICS
101 - Chapter 12 From reachability distance to clustering
102 - Chapter 12 Hierarchical clustering
103 - Chapter 12. Evaluating clustering results - Evaluation metrics
104 - Chapter 13 Parallel clustering - MapReduce and canopy clustering
105 - Chapter 13 Canopy clustering
106 - Chapter 13 MapReduce
107 - Chapter 13 First map, then reduce
108 - Chapter 13 MapReduce k-means
109 - Chapter 13 Parallelizing canopy clustering
110 - Chapter 13 MapReduce canopy clustering
111 - Chapter 13 MapReduce DBSCAN - Part 1
112 - Chapter 13 MapReduce DBSCAN - Part 2
113 - Part 3. Planar graphs and minimum crossing number
114 - Chapter 14 An introduction to graphs - Finding paths of minimum distance
115 - Chapter 14 Implementing graphs
116 - Chapter 14 Graph properties
117 - Chapter 14 Graph traversal - BFS and DFS
118 - Chapter 14 Reconstructing the path to target
119 - Chapter 14 Shortest path in weighted graphs - Dijkstra
120 - Chapter 14 Beyond Dijkstras algorithm - A
121 - Chapter 14 How good is A search
122 - Chapter 14 Heuristics as a way to balance real-time data
123 - Chapter 15 Graph embeddings and planarity - Drawing graphs with minimal edge intersections
124 - Chapter 15 Some basic definitions
125 - Chapter 15 Planar graphs
126 - Chapter 15 Planarity testing
127 - Chapter 15 Improving performance
128 - Chapter 15 Non-planar graphs
129 - Chapter 15 Rectilinear crossing number
130 - Chapter 15 Edge intersections
131 - Chapter 15 Polylines
132 - Chapter 15 Intersections between quadratic Bezier curves
133 - Chapter 16 Gradient descent - Optimization problems (not just) on graphs
134 - Chapter 16 Did you just say heuristics
135 - Chapter 16 How optimization works
136 - Chapter 16 Gradient descent
137 - Chapter 16 When is gradient descent appliable
138 - Chapter 16 Applications of gradient descent
139 - Chapter 16 Gradient descent for graph embedding
140 - Chapter 17 Simulated annealing - Optimization beyond local minima
141 - Chapter 17 Sometimes you need to climb up to get to the bottom
142 - Chapter 17 Why simulated annealing works
143 - Chapter 17 Short-range vs long-range transitions
144 - Chapter 17 Simulated annealing + traveling salesman
145 - Chapter 17 Exact vs approximated solutions
146 - Chapter 17 State transitions
147 - Chapter 17 Simulated annealing and graph embedding
148 - Chapter 17 Force-directed drawing
149 - Chapter 18 Genetic algorithms - Biologically inspired, fast-converging optimization
150 - Chapter 18 Inspired by nature
151 - Chapter 18 Chromosomes
152 - Chapter 18 Natural selection
153 - Chapter 18 Selecting individuals for mating
154 - Chapter 18 Crossover
155 - Chapter 18 The genetic algorithm template
156 - Chapter 18 TSP
157 - Chapter 18 Results and parameters tuning
158 - Chapter 18 Minimum vertex cover
159 - Chapter 18 Other applications of the genetic algorithm
160 - Chapter 18 Beyond genetic algorithms
161 - Appendix A. A quick guide to pseudo-code
162 - Appendix A Conditional instructions
163 - Appendix A Blocks and indent
164 - Appendix B. Big-O notation
165 - Appendix B Notation
166 - Appendix C. Core data structures
167 - Appendix C Tree
168 - Appendix C Hash table
169 - Appendix D. Containers as priority queues
170 - Appendix E. Recursion
171 - Appendix E Tail recursion
172 - Appendix F. Classification problems and randomnized algorithm metrics
173 - Appendix F Classification metrics